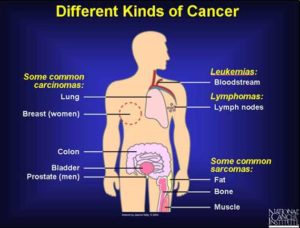
Cancer is a term used for diseases in which abnormal cells divide without control and are able to invade other tissues. Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body through the blood and lymph systems. Cancer is not just one disease but many diseases. There are more than 100 different types of cancer. (What is Cancer?)
Mushrooms have been consumed for their health benefits for thousands of years in China, and the main active component was recently identified as beta-glucan. Beta glucans (β-glucans) are polysaccharides – long chains of sugar molecules – found on the surface of microorganisms such as bacteria and yeast, as well as in some plants and edible fungi such as mushrooms. Natural foods containing β-glucans, including Shitake mushrooms, have been used for centuries for treating both infectious diseases and cancer in traditional Asian medicine, but with mixed success.
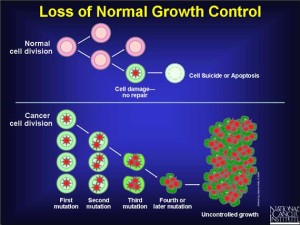 The immune-stimulating effect of beta-glucans has been well studied, and several beta-glucan receptors have been identified on the surface of immune cells. In addition, mushroom extracts with high levels of beta-glucans have also been shown to have direct cytotoxic effects on cancer cells, and beta-glucans are used for the treatment of cancer.
The immune-stimulating effect of beta-glucans has been well studied, and several beta-glucan receptors have been identified on the surface of immune cells. In addition, mushroom extracts with high levels of beta-glucans have also been shown to have direct cytotoxic effects on cancer cells, and beta-glucans are used for the treatment of cancer.
A bioactive beta-glucan from the Maitake mushroom has a cytotoxic effect, presumably through oxidative stress, on prostatic cancer cells in vitro, leading to apoptosis. Based on in vitro studies, beta-glucans act on several immune receptors including Dectin-1, complement receptor (CR3) and TLR-2/6 and trigger a group of immune cells including macrophages, neutrophils, monocytes, natural killer cells and dendritic cells.
SOURCE:
Anti-cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry – Bentham Science Publishers