Total Rebuild of The Body’s Defense System TM
 β-glucans are sugars that are found in the cell walls of the bacteria, fungi, yeasts, algae, lichens, and plants, such as oats and barley. They are sometimes used as medicine. β-glucans are used for high cholesterol, diabetes, cancer, and HIV/AIDS. β-glucans are also used to boost the immune system in people whose body defense has been weakened by conditions such the chronic fatigue syndrome, or physical and emotional stress; or by treatments such as radiation or chemotherapy. β-glucans are also used for colds (common cold), flu (influenza), H1N1 (swine) flu, allergies, hepatitis, Lyme disease, asthma, ear infections, aging, ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, fibromyalgia, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis. Healthcare providers sometimes give β-glucans by IV (intravenously) or by injection into the muscle, to treat cancer and to boost the immune system in people with HIV/AIDS and related conditions. β-glucans are also given by IV to prevent infection in people, after surgery. Healthcare providers sometimes give beta glucans via a shot under the skin (subcutaneously) for treating and reducing the size of skin tumors resulting from cancer that has spread. (US National Library of Medicine)
β-glucans are sugars that are found in the cell walls of the bacteria, fungi, yeasts, algae, lichens, and plants, such as oats and barley. They are sometimes used as medicine. β-glucans are used for high cholesterol, diabetes, cancer, and HIV/AIDS. β-glucans are also used to boost the immune system in people whose body defense has been weakened by conditions such the chronic fatigue syndrome, or physical and emotional stress; or by treatments such as radiation or chemotherapy. β-glucans are also used for colds (common cold), flu (influenza), H1N1 (swine) flu, allergies, hepatitis, Lyme disease, asthma, ear infections, aging, ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, fibromyalgia, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis. Healthcare providers sometimes give β-glucans by IV (intravenously) or by injection into the muscle, to treat cancer and to boost the immune system in people with HIV/AIDS and related conditions. β-glucans are also given by IV to prevent infection in people, after surgery. Healthcare providers sometimes give beta glucans via a shot under the skin (subcutaneously) for treating and reducing the size of skin tumors resulting from cancer that has spread. (US National Library of Medicine)
Numerous animal and human studies have demonstrated the efficacy of beta glucan in:
- Preventing and fighting post-surgical infections, antibiotic-resistant infections and sepsis.
- Treating cardiovascular disease, lowering cholesterol and reversing arteriosclerosis.
- Stimulating the immune system to destroy cancer cells.
- Speeding tissue regeneration and repair, particularly stimulating wound healing of diabetic and venous stasis ulcers.
- Enhancing the formation of white blood cells (hematopoiesis) in patients undergoing radiation and chemotherapy or recovering from bone marrow transplants.
- Creating targeted drug- and antigen-delivering systems.
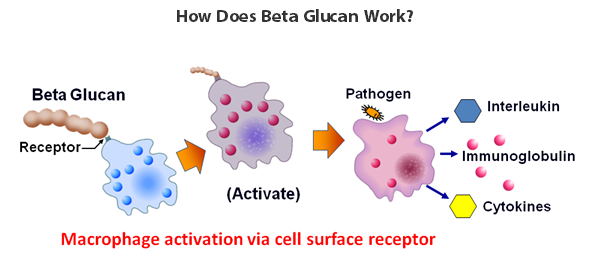
Beta glucan works to stimulate the two main components of the body’s immune system, the innate and the acquired immune systems. In the innate immune system, beta glucan binds with the macrophages, a type of white blood cell whose job is to detect bacteria, viruses and other pathogens and coordinate the body’s defenses against them. When activated by beta glucan, macrophages have an increased ability to identify and destroy foreigner intruders. After devouring pathogens through a process called phagocytosis, the macrophages then communicate the intruder’s presence to the body’s other defenders. Research shows that macrophages fortified by beta glucan are better able to rally the body’s defenses.
Now the acquired immune system joins the fight. Using the information transmitted from the macrophages, the acquired immune system learns to manufacture other killer cells and blood factors designed to defend against a specific attack. These include B-cells, which produce antibodies and killer T-cells. The antibodies, working with the innate immune system, destroy foreigners and bind them into clusters, which are then engulfed by macrophages. This is how the body rids itself of infection and disease.
Medicinal Mushrooms
The healing and immunostimulating properties of mushrooms have been known for thousands of years in the Eastern countries. These mushrooms contain biologically active polysaccharides that mostly belong to group of beta-glucans. These substances increase host immune defense by activating complement system, enhancing macrophages and natural killer cell function.

Increased interest in β-glucan in the last two decades arises from its functional and bioactive properties. Of all fibers, its health benefits have been the most extensively documented, and the use of health claims with β-glucan-containing foods has been allowed in several countries including Canada, the United States of American, Sweden, Finland, and the United Kingdom.
- Beta Glucan vs. Cancer
- Beta Glucan vs. high Blood Cholesterol
- Beta Glucan vs. Periodontal Disease
- Beta-glucan vs. Allergies
- Beta Glucan vs. Diabetes and associated cardiovascular risks
- Beta Glucan vs. Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
SOURCES:
Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research
US National Library of Medicine